Let’s be honest. Every trader has been there: you experience a great winning streak, feel invincible, and then a series of losses wipes out your gains and your confidence. You’re left staring at your screen, wondering, “What’s the root cause of my recurring trading blunders?”
This frustrating cycle is the reality for traders who fly blind. But what if you had the “black box” flight recorder for your trading? A tool that captures every decision, thought, and outcome, allowing you to learn, adapt, and finally break the cycle. That tool is a trading journal.
In this guide, I will fully answer the question, What is a trading journal?, explain why it’s non-negotiable, and show you how to start using one today.
Key takeaways:
- What is a trading journal? It is your “black box” that records both objective trade data and subjective thoughts and emotions.
- A trading journal turns feelings into hard data, building discipline and proving your strategy’s statistical edge.
- How to structure it: Divide each entry into three parts: a plan before the trade, execution notes during the trade, and a review after the trade.
- Choose a format that suits your style, from a simple notebook to a spreadsheet or dedicated software.
- The biggest trap is not reviewing your journal, which is where the actual learning and improvement occur.
1. What is a trading journal?
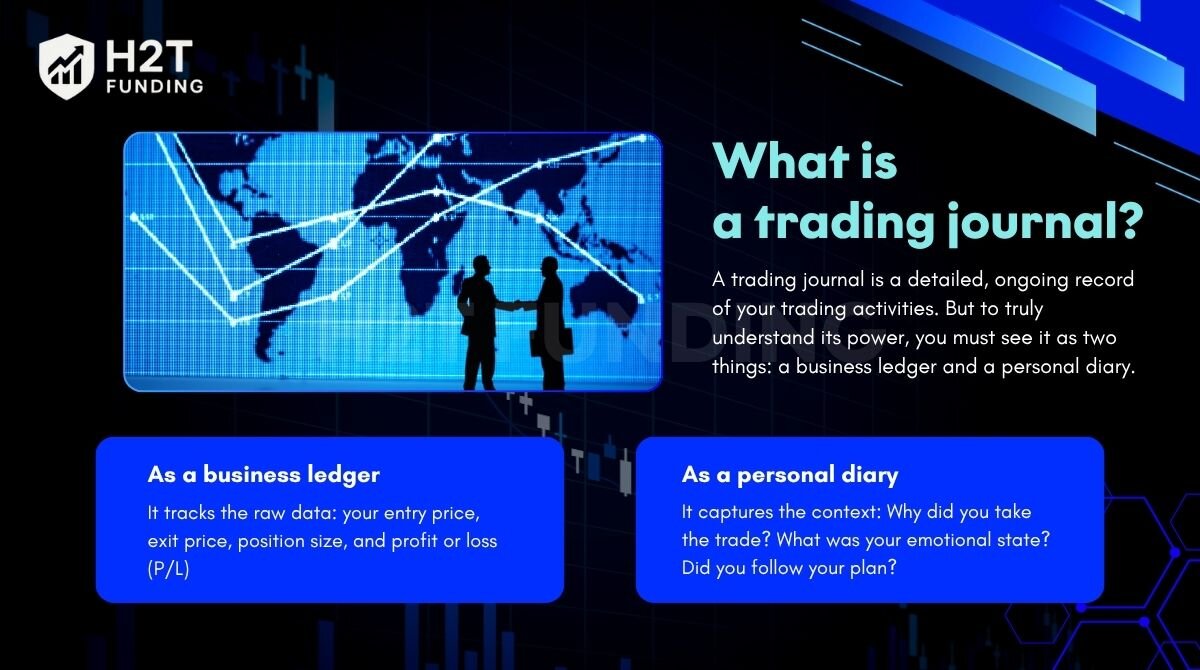
A trading journal is a detailed, ongoing record of your trading activities. But to truly understand its power, you must see it as two things: a business ledger and a personal diary.
- As a business ledger, it tracks the raw data: your entry price, exit price, position size, and profit or loss (P/L). This is the objective “what.”
- As a personal diary, it captures the context: Why did you take the trade? What was your emotional state? Did you follow your plan? This is the subjective “why” and “how.”
How is this different from my broker’s history?
Your broker’s statement is like a bank statement; it shows transactions but tells you nothing about your spending habits. A trading journal is like a complete financial plan. It forces you to justify every decision and analyze the behavior behind the numbers.
2. Introduce 3 types of trading journals
When we talk about types of trading journals, it usually refers to the format or method you use to keep your journal, as the content you put in them is generally similar.
Here are the 3 main types:

2.1. Physical (Notebook) journal
A traditional pen-and-paper notebook where you manually write down all your trade details, thoughts, and analysis.
- Pros: Very personal, no screen distractions, can foster deeper reflection through handwriting.
- Cons: Hard to analyze data quickly, no automated calculations, easy to lose or damage, not easily searchable.
- Best for: Traders who prefer a tactile experience, want to minimize screen time, or are just starting out with a very simple approach.
2.2. Spreadsheet journal (e.g., Excel, Google Sheets)
A digital spreadsheet where you manually enter trade data into columns and rows. You can use formulas for basic calculations (P/L, win rate).
- Pros: Customizable, free (or low cost with existing software), allows for basic data analysis and simple charting.
- Cons: Manual data entry can be time-consuming, limited advanced analytics, can get messy with lots of trades, and no automated imports.
- Best for: Traders who are comfortable with spreadsheets, want more organization than a physical notebook but aren’t ready for dedicated software, or have a moderate number of trades.
2.3. Dedicated trading journal software/apps
Specialized online platforms or applications designed specifically for trading journaling. Examples include Edgewonk, TraderSync, Tradervue, TradeZella, etc.
- Pros: Automated trade imports from brokers, advanced analytics (win rate by strategy, time of day, etc.), detailed charts and reports, psychological tracking features, cloud storage, and often include chart markups.
- Cons: Can be expensive (subscription fees), may have a learning curve for all the features.
- Best for: Serious traders looking for in-depth analysis, saving time on data entry, identifying complex patterns, and gaining psychological insights into their trading behavior.
3. Why keeping a journal is non-negotiable for serious traders
Once you understand the answer to “what is a trading journal,” the next logical question is why it’s so critical. A business-like approach to the markets is essential for any trader whose goal is to get funded and achieve long-term profitability. And no successful business operates without meticulous record-keeping. Here’s how a journal gives you an undeniable edge.
3.1. It turns vague feelings into hard data
You might feel like you’re good at trading news events. Your journal will prove or disprove that feeling with cold, hard numbers. After a month of journaling, you might discover a clear pattern: 80% of your profits come from trading trend continuations on the 1-hour chart, while you consistently lose money trying to catch falling knives on lower timeframes. This insight alone is priceless.
3.2. It’s essential for developing your emotional discipline
The biggest battle in trading is the one fought between your ears. A journal is your arena for that fight. By writing down your emotions (fear, greed, FOMO, anger after a loss), you externalize them. You can see them for what they are, dangerous impulses, and learn to control them.
3.3. It proves if your strategy actually works
Every profitable strategy has a statistical “edge.” Your journal is the only way to know if your strategy has an edge in real-world market conditions. If you can’t prove it on paper, you’re not trading, you’re gambling.
3.4. It builds unshakeable discipline and accountability
When you know you have to log every trade, you’re far less likely to break your rules. It forces you to ask, “Will I be proud to write this trade down later?” This simple question can be the difference between a disciplined entry and an impulsive mistake.
See more helpful articles:
4. A practical guide to building and using your trading journal
Ready to get started? Here’s a practical, three-step process.

4.1. Step 1: Choose your tool
You have three main options. The best one is the one you’ll actually use consistently.
- A physical notebook: Simple and effective. The physical act of writing can help reinforce lessons.
- A spreadsheet (Excel or Google Sheets): This is the most recommended starting point. It’s free, customizable, and allows for easy data sorting and analysis.
- Specialized software: Apps like Tradervue or TraderSync are powerful, but they come with a subscription fee.
4.2. Step 2: Structuring your journal entries for maximum insight
For your journal to be effective, each entry needs to capture the full story of the trade. Divide it into three parts.
4.2.1. Part 1: The plan (pre-trade)
This is the stage where you meticulously prepare everything, documenting what’s necessary before taking any action. It helps you gain a clear understanding of your initial intentions and the rationale behind the upcoming trade.
- Date & asset: e.g., 2024-10-25, XAU/USD.
- Setup/Strategy: Be specific. e.g., “Bearish Engulfing at Daily Resistance.”
- The “why”: Your 1-2 sentence thesis for the trade.
- Entry, stop-loss (SL), take-profit (TP): Your exact price levels.
- Risk/reward (R:R) ratio: e.g., 1:3.
4.2.2. Part 2: The execution (during-trade)
In this section, you’ll quickly log what happened during the trade. This helps you track emotional responses and any mistakes that might occur in real-time, providing a basis for later analysis.
- Emotions: One word is fine. e.g., “Confident,” “Anxious,” “FOMO.” Be brutally honest.
- Mistakes made? e.g., “Entered slightly late,” “Used too much size.”
4.2.3. Part 3: The autopsy (post-trade)
This is the most critical part, where you look back at the entire process to extract valuable lessons. Thorough post-trade analysis will help you better understand your performance and make necessary adjustments for future improvement.
- Exit price & P/L: The final result in dollars, percentage, and R-multiple.
- Screenshot of the chart: This is non-negotiable. A picture prevents hindsight bias and shows you exactly what you saw.
- The core lesson: If I could distill this trade into one core lesson, what would it be?
4.3. Step 3: The weekly review
A journal you don’t review is worthless. Commit to a one-hour performance review each weekend to analyze your trading from a high-level perspective. Open your journal and ask these questions:
- What was my overall performance for the week, measured in R-multiples?
- What was my single biggest win, and why did it work?
- What was my single dumbest mistake, and how can I prevent it next week?
- What patterns do my winning trades have in common?
- Based on this data, what is the #1 thing I need to focus on improving next week?
5. What should be included in a trading journal?
Keeping a trading journal is smart for any trader. It’s not just about recording wins and losses; it’s a powerful tool for self-discovery and improvement. By consistently tracking your trades, you can learn from every decision and truly understand what makes you a better trader.
Here’s what you should include for each trade:
- The basics:
- Date and time: When you entered and exited.
- What you traded: The specific stock, crypto, or other asset.
- Buy or sell: Were you going long or short?
- How much: Your position size.
- Prices: Your exact entry and exit prices.
- Stop loss/take profit: Your planned exit points.
- Profit/loss: How much money you made or lost.
- Fees: Any costs involved.
- Your plan & why:
- Strategy: What trading method did you use?
- Reason for trade: Why did you enter? What did you see on the chart or in the news that made you take the trade?
- Market vibe: How was the overall market looking? (e.g., “strong uptrend,” “choppy”)
- Chart screenshot: A picture of your chart, marked up with your entry, exit, and key levels.
- Your headspace:
- Emotions: How did you feel before, during, and after the trade? (e.g., “confident,” “stressed,” “patient”)
- Discipline check: Did you stick to your plan? If not, why?
- Lessons learned:
- What went right/wrong: Be honest about why the trade succeeded or failed.
- Key takeaways: What can you learn from this trade to improve next time?
6. Suggest some top trading journal software
While a spreadsheet is a fantastic starting point, dedicated software can save you time and provide deeper analytical insights. These platforms often import your trades automatically from your broker and generate powerful reports. Here are a few of the most reputable options in the industry:
6.1. Tradervue
Often considered the industry standard. It’s renowned for its powerful analytics and filtering capabilities, allowing you to slice and dice your data in countless ways. It has a great free plan for beginners and paid tiers for more advanced features like risk analysis and automated reporting.

6.2. TraderSync
A strong competitor to Tradervue, known for its modern, intuitive interface and mobile app. It excels at tracking performance targets and includes unique features like a simulator to practice what you’ve learned from your journal.
6.3. Edgewonk
This is more than just a journal; it’s a complete trading psychology coach. Edgewonk focuses heavily on identifying and correcting behavioral patterns and discipline issues. It doesn’t auto-import trades, which it views as a feature to force mindful, deliberate journaling.
6.4. Kinfo
A more social and lightweight option. Kinfo turns your trading performance into shareable stats and allows you to follow other traders. It’s great for transparency and tracking basic metrics, though it lacks the deep analytical power of the options above.
6.5. Microsoft Excel (or Google Sheets)
You don’t always need fancy software to start. A simple spreadsheet like Excel (or free Google Sheets) can be incredibly powerful. You build your own system, meaning total customization. You’ll enter everything manually, but for many, it’s the perfect flexible and free solution.
6.6. Trademetria
Trademetria stands out for its strong focus on statistical analysis and advanced reporting. It’s built for traders who want to dive deep into their numbers and find an edge. Beyond basic logging, it helps you analyze performance by time of day, day of the week, and specific setups.
6.7. TradesViz
TradesViz offers a comprehensive suite of tools for serious traders. It’s known for its detailed charting capabilities, letting you easily annotate trades directly on interactive charts. What makes it especially useful is its extensive analytics, including multi-strategy comparisons and portfolio analysis. It supports many brokers for seamless trade imports.
7. The traps that cause 90% of traders to fail at journaling
Avoid these common mistakes that render a journal useless.
- The “good grades only” journal: Only logging wins is lying to yourself. You learn more from a well-analyzed loss than from an accidental win.
- Being vague: Entries like “bought gold, lost money” are useless. You need the “why” and the specific data points to learn anything.
- Dishonesty: Your journal is a judgment-free zone. If you entered a trade out of pure revenge, write it down. Acknowledging a flaw is the only way to fix it.
- The biggest trap: Never reviewing it! Data collection is not data analysis. The learning doesn’t happen when you write; it happens when you review.
8. Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
Your trading plan acts as a roadmap, laid out before you begin your journey. A trading journal is the travel log you write during and after the journey. You need both to succeed.
The most common reasons are: you’re collecting data but not analyzing it, you’re not being 100% honest with yourself, or you’re identifying problems but not implementing solutions.
Don’t abandon the project! The goal is consistency, not perfection. Simply acknowledge the gap and start again with the very next trade.
No, but the journal often evolves. An experienced trader will always track their performance data. It remains a vital tool for managing their statistical edge at every stage of their career.
A trading journal helps you record and analyze your trades, track performance, identify decision-making patterns, and refine your strategy. It’s a key tool for self-assessment and continuous improvement in trading.
A trade journal can be a notebook, a spreadsheet (like Excel), or specialized software. A simple example might include columns for date, asset, entry/exit prices, profit/loss, and reasons for the trade.
You should write objective trade data (e.g., prices, position size, P&L) and subjective observations (e.g., reasons for entry/exit, your emotions, and lessons learned). Include pre-trade analysis, execution details, and post-trade review.
Choose a format, define your metrics, and be consistent in recording every trade. Be honest about your emotions and mistakes, and review regularly to identify patterns and adjust your strategy.
Yes, trading journals are highly effective. They help you gain self-awareness, identify strengths and weaknesses, measure progress, improve discipline, and accelerate your learning from every trade.
9. Conclusion: The choice is yours
In trading, you can rely on hope and luck, or you can rely on strategies and discipline. A trading journal is the tool that facilitates this second path. It’s the line that separates hobbyists who lose money from professionals who build careers. The process takes effort, but the payoff is immeasurable: clarity, confidence, and consistency.
Make the decision today to start treating your trading like a business. Now that you have a complete answer to “what is a trading journal?” and understand the power it holds, the only thing left is to begin.
Follow H2T Funding to read more useful information in our Prop Firm & Trading Strategies section.