Today’s quantitative trading scene is dominated by industry giants like Jane Street, Two Sigma, and Optiver, who are pushing the boundaries of finance. Their edge comes from data-driven strategies, using automation to execute trades in mere milliseconds. Trading everything from equities to crypto, they are fundamental to modern market liquidity and risk management.
In this article, H2T Funding presents a detailed list of best quantitative trading firms, including the biggest names and emerging AI-driven players. You’ll learn how these firms operate and what makes them successful.
Key takeaways
- Quantitative trading firms use algorithms, data, and automation to trade efficiently across multiple markets.
- High-frequency, proprietary, systematic, and market-making firms each play distinct roles in liquidity, risk management, and market efficiency.
- Leading quant firms combine advanced technology, low-latency execution, and rigorous risk control to capture small price inefficiencies.
- Crypto and AI-driven firms adapt quantitative strategies to digital assets and next-generation trading models.
- Trader performance is evaluated on profitability, risk management, execution efficiency, and strategy innovation.
- Consistency, disciplined workflows, and automation are key to long-term success in quantitative trading.
1. What are quantitative trading firms?
Think of quant trading firms as financial companies that let computers and data do the talking. Rather than a person making a judgment call, they use algorithms and automated systems to spot trading chances based on pure analysis.

If you’re exploring funded trading opportunities, you may also want to learn how to choose a prop firm for safer and more strategic participation.
Their traders, or quants, are experts who create strategies to profit from tiny, split-second market movements. Because it’s all automated, thousands of trades can happen in the blink of an eye, that’s high-frequency trading (HFT) in a nutshell.
If you’re looking at funded trading programs, knowing this can help you pick a prop firm that trades in a safer, more calculated way. By operating this way, they play a huge role in keeping markets active and fair.
2. Key types & categories of quantitative trading firms
Not all quant firms are the same. We can generally break them down into a few key types based on their trading speed, their style, and how they’re funded. Knowing the difference is important because each type plays a unique role in how modern markets work.

For new traders, learning the core prop firm rules can also provide useful context for how these firms manage risk and structure participation.
2.1. High-Frequency Trading (HFT) Firms
HFT firms focus on executing trades within microseconds, relying heavily on low-latency infrastructure and optimised algorithms. Their goal is to capture very small, short-lived price differences that appear and disappear within milliseconds.
These firms require advanced coding, network optimisation, and data engineering to stay ahead of competitors. Profit margins per trade are small, but cumulative returns can be significant due to enormous trade volumes.
HFT strategies also contribute to market liquidity, though they demand constant monitoring and risk control. Understanding the four major trading sessions helps contextualise when liquidity peaks, even though HFT operates 24/7 across global markets.
2.2. Proprietary Trading Firms (Prop Firms)
Proprietary trading firms operate using their own capital rather than client funds. This independence allows them to take higher risks and adopt flexible strategies such as arbitrage, intraday trading, and short-term market making.
Traders in prop firms often share directly in the profits they generate, supported by flexible compensation structures that reward performance and adaptability.
Decision-making tends to be fast, data-driven, and adaptive to changing market conditions. Technology and algorithmic execution remain central, but human oversight is still crucial for strategic alignment and risk control.
Success in these environments often depends on a trader’s ability to maintain discipline in trading, especially when dealing with high leverage or rapid market shifts.
2.3. Hedge Funds (Systematic & Multi-Manager)
Systematic hedge funds apply quantitative models to manage diversified portfolios. These funds typically trade across asset classes and timeframes, from minutes to months. Multi-manager structures divide capital among smaller teams, each responsible for a distinct trading strategy under strict risk parameters. They also maintain a transparent compensation structure linked to long-term, risk-adjusted returns.
Their focus is on portfolio optimisation, alpha generation, and consistent long-term returns. Machine learning, statistical arbitrage, and factor-based investing are common approaches. These firms often combine large-scale computing power with deep financial expertise to uncover predictive market patterns.
2.4. Asset Managers & Investment Firms
Traditional asset managers are increasingly using quantitative methods to enhance portfolio design and risk management. Unlike HFTs or prop firms, their trading frequency is lower, emphasising systematic investment, factor exposure, and portfolio diversification.
Quant teams in these firms develop models for asset allocation, volatility forecasting, and performance attribution. The goal is to generate stable returns over time rather than exploiting short-term inefficiencies. This quantitative integration has redefined how large institutions approach active and passive investing.
2.5. Quantitative Market-Making Firms
Market-making firms provide liquidity by continuously offering buy and sell quotes for a wide range of instruments. Their systems depend on real-time pricing algorithms that adjust instantly to market movements.
Profit comes primarily from the bid-ask spread, but effective risk management and hedging are essential to remain profitable in volatile markets. These firms play a vital role in maintaining smooth trading conditions, ensuring that other participants can execute orders efficiently at fair prices.
Each of these firm types contributes uniquely to market structure. Together, they form an ecosystem that balances speed, efficiency, capital, and innovation, driving the evolution of global quantitative trading.
3. How does a quantitative trading firm work?
A quantitative trading firm functions through a structured, technology-driven workflow that removes emotional decision-making and replaces it with data, models, and automation.
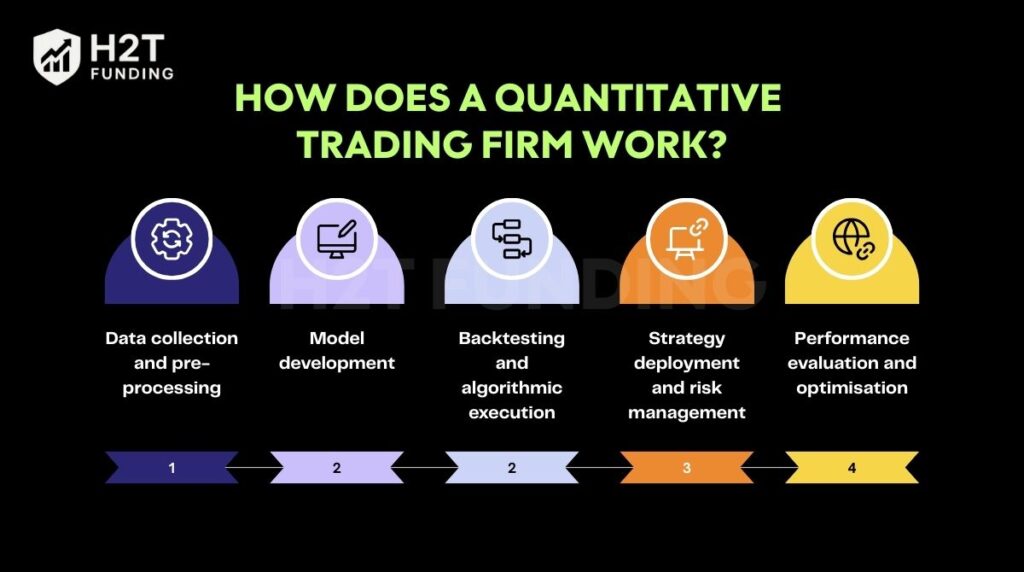
Most firms follow a standardised pipeline: Data Collection -> Model Development -> Backtesting -> Deployment -> Monitoring. This ensures every decision is consistent, testable, and scalable.
- Data collection and pre-processing: Firms gather massive amounts of market, economic, and alternative data, ranging from prices and volumes to sentiment, macroeconomic indicators, and even weather reports. This information is cleaned and standardised so algorithms can identify meaningful patterns that may signal trading opportunities.
- Model development: Quant researchers design mathematical and quantitative models that forecast asset movements. These models are coded into algorithms and tested against historical data to assess potential performance.
- Backtesting and algorithmic execution: Backtesting ensures a strategy works reliably before real capital is used. Once approved, algorithms are deployed through low-latency systems that place and cancel orders within milliseconds. Execution is monitored to control slippage, transaction costs, and timing, maintaining efficiency.
- Strategy deployment and risk management: Validated algorithms are deployed through automated systems that execute orders rapidly and precisely. Automated risk controls set position limits, leverage, and drawdown thresholds, while tools like VaR and stress tests monitor exposure. Human oversight remains crucial to handle anomalies or sudden market shocks.
- Performance evaluation and optimisation: After each trading session, results are analysed using metrics such as Sharpe ratio, Alpha, and win-loss ratios. Underperforming algorithms are refined or retrained with updated data, keeping strategies adaptive and competitive.
A quantitative trading firm represents the fusion of finance, mathematics, and computer science. By transforming data into executable insight, it achieves speed, accuracy, and discipline beyond human capability, the foundation of modern algorithmic finance.
4. 100+ Leading quantitative trading firms in 2026
Proprietary and market-making firms are the engine of modern electronic markets. These companies trade their own capital, specialising in options, derivatives, ETFs, and high-frequency trading (HFT). Their algorithms constantly quote buy and sell prices across exchanges, ensuring liquidity and price efficiency.
What sets them apart is the fusion of quantitative research, low-latency execution, and risk modelling, a formula that allows them to profit from micro-price movements while supporting market stability.

4.1. Proprietary & Market-Making Firms
The biggest quantitative trading firms in the proprietary and market-making sector form the core of modern electronic markets. They trade using their own capital and rely on data, algorithms, and high-performance infrastructure.
Their business revolves around options, futures, ETFs, and derivatives, providing liquidity and ensuring price stability. These firms merge quantitative research, real-time execution, and risk control, turning tiny price discrepancies into consistent profits.
1. Jane Street – United States
Headquartered in New York, Jane Street is one of the most advanced prop trading firms in the world. The firm operates across equities, ETFs, options, and fixed income, using complex algorithms to manage risk and liquidity.
Jane Street is known for its strong academic culture and rigorous quantitative hiring standards. It trades across major exchanges in the US, Europe, and Asia, serving as a key player in the global ETF market.
2. Jump Trading – United States
Based in Chicago, Jump Trading focuses on high-frequency and algorithmic trading across global markets. It operates in futures, options, and digital assets, with exceptionally low-latency systems.
Its crypto division, Jump Crypto, is a leading digital asset liquidity provider. Jump’s reputation comes from its technological innovation and research-driven approach.
3. DRW Trading – United States
DRW is a Chicago-based multi-asset proprietary firm active in derivatives, fixed income, and crypto. Its subsidiary, Cumberland, ranks among the largest crypto market makers worldwide.
The firm combines strategic risk-taking, innovation, and diversification, supported by strong capital discipline. DRW also invests in fintech and blockchain ventures through its capital arm.
4. Optiver – Netherlands
Optiver, founded in Amsterdam in 1986, is one of Europe’s most respected market-making firms. It trades options, futures, and ETFs, ensuring liquidity across major exchanges.
The firm emphasises discipline, risk awareness, and continuous improvement, backed by advanced infrastructure. Optiver’s offices in Sydney, Chicago, and Singapore reflect its global reach and technical excellence.
5. IMC Financial Markets – Netherlands
IMC is a leading global market maker headquartered in Amsterdam. It operates across 100+ venues, trading derivatives, ETFs, and equities. Its strength lies in combining data-driven decision-making with agile technology. IMC’s teams continually refine algorithms to stay efficient in fast-moving, volatile markets.
6. Flow Traders – Netherlands
Flow Traders is an electronic liquidity provider specialising in ETFs and exchange-traded products. It maintains offices in Amsterdam, New York, and Hong Kong.
The firm’s technology-driven execution ensures tight spreads and efficient pricing for institutional investors. Flow Traders also applies its expertise to digital assets and crypto ETPs, bridging traditional and blockchain markets.
7. Hudson River Trading (HRT) – United States
HRT combines computer science and quantitative finance to power automated trading strategies. Based in New York, it operates across equities, futures, and digital assets.
The firm promotes a performance-driven culture, a research-heavy culture where engineers and quants co-develop models and systems. Its infrastructure supports millisecond-level decision-making in global markets.
8. Tower Research Capital – United States
Founded in 1998, Tower Research Capital is known for high-frequency trading and low-latency execution. Its operations span equities, futures, and FX across major global markets.
Tower’s strength lies in custom hardware, predictive modelling, and advanced infrastructure. It continuously refines algorithms to capitalise on short-lived market inefficiencies.
9. Citadel Securities – United States
Citadel Securities is a global market-making powerhouse serving institutional clients, brokers, and exchanges. It provides liquidity in equities, options, and fixed income. The firm’s edge comes from its analytics, capital efficiency, and risk control systems. Citadel’s presence on the NYSE and NASDAQ reinforces its role as a key liquidity provider.
10. XTX Markets – United Kingdom
London-based XTX Markets is a systematic market maker active in FX, equities, and commodities. Its algorithms leverage machine learning and model-based pricing to improve execution quality. XTX’s transparent and research-led approach has set new standards for liquidity and fairness in electronic markets, particularly in Europe and Asia.
11. Virtu Financial – United States
Virtu is a publicly traded liquidity provider combining proprietary trading with client execution. It operates globally across equities, options, and fixed income. The firm’s infrastructure enables real-time analytics and optimal routing, ensuring best execution. Virtu’s acquisition of ITG expanded its reach into execution services and data analytics.
12. Akuna Capital – United States
Akuna Capital, based in Chicago, is a derivatives market maker focused on options and volatility trading. It empowers traders to design and test strategies with autonomy. The firm’s strength lies in options pricing and volatility modelling, allowing it to thrive in both calm and turbulent markets.
13. Five Rings Capital – United States
Five Rings Capital is a New York-based proprietary firm emphasising collaboration and speed. It trades across equities, options, and futures with a research-first mindset. Its culture fosters innovation and knowledge sharing, making it a training ground for new quantitative talent and competitive strategy design.
14. Susquehanna International Group (SIG) – United States
SIG, headquartered in Pennsylvania, is one of the world’s largest privately held trading firms. It excels in options pricing and market-making, using game theory and probability modelling. SIG’s structured training and diversified global presence make it a standout in ETF and options arbitrage.
15. TransMarket Group (TMG) – United States
TMG is a Chicago-based prop trading firm with decades of experience in futures and options. It applies systematic and discretionary approaches to arbitrage opportunities. The firm’s longevity comes from consistent risk management and a disciplined, research-driven culture that adapts to new asset classes and markets.
16. DV Trading – United States
DV Trading operates across equities, energy, commodities, and fixed income markets. It blends algorithmic models with discretionary strategies for balanced risk exposure. The firm’s adaptive systems and quantitative mindset allow it to maintain stability and performance across volatile cycles.
17. Bluefin Trading – United States
Bluefin Trading operates as a multi-asset proprietary trading firm with expertise in options, futures, and equities. Based in New York and Chicago, it is known for its collaborative trading desks and a hybrid approach combining discretionary insights with automated systems. The firm’s strength lies in its ability to adjust quickly to volatile derivatives markets.
18. Volant Trading – United States
Volant Trading is a highly specialised options market maker focused on equity and index derivatives. It leverages advanced pricing models and high-speed infrastructure to maintain consistent liquidity across U.S. exchanges. Volant is recognised for its tight risk controls and quantitative strategy development.
19. Old Mission Capital – United States
Old Mission Capital is a global ETF market maker that supports efficient trading across both equities and fixed income ETFs. Its expertise lies in pricing and hedging complex exchange-traded instruments, using proprietary risk systems to keep spreads competitive. The firm’s data-centric execution makes it a critical player in the ETF ecosystem.
20. Group One Trading – United States
Group One Trading is an options market maker headquartered in Chicago. It operates on major U.S. exchanges, providing liquidity for equity and index options. Known for its risk-neutral approach and efficient hedging, Group One maintains a strong presence on the CBOE and NYSE Arca.
21. Tradebot Systems – United States
Tradebot Systems, based in Kansas City, is a pioneer in equity high-frequency trading (HFT). The firm focuses on ultra-fast execution and order routing algorithms in U.S. equities. With millisecond-level speed and low overhead, Tradebot exemplifies the power of automation in market-making for single stocks.
22. Chicago Trading Company (CTC) – United States
CTC is a derivatives trading firm active in options, futures, and fixed income. It combines quantitative models with trader intuition to manage risk across multiple asset classes. CTC’s longevity in the options market underscores its expertise in volatility pricing and market structure optimisation.
23. Belvedere Trading – United States
Belvedere Trading, headquartered in Chicago, focuses on options and derivatives market-making. It uses proprietary risk and volatility models to trade across major exchanges. The firm fosters a collaborative environment where quants, engineers, and traders co-develop pricing systems for dynamic market conditions.
24. Eclipse Trading – Hong Kong
Eclipse Trading is a leading options market maker in Asia, operating primarily in Hong Kong, Tokyo, and Sydney. It specialises in equity and index derivatives, providing liquidity to regional exchanges. Its strength lies in technology integration and efficient hedging in less liquid Asian markets.
25. Maven Securities – United Kingdom
London-based Maven Securities operates as a proprietary and market-making firm across derivatives and equities. It is known for its rigorous risk management and strong technical infrastructure. Maven combines quantitative modelling and discretionary oversight to balance speed with stability in global markets.
26. Valkyrie Trading – United States
Valkyrie Trading is a Chicago-based options proprietary firm specialising in equity derivatives and volatility products. It focuses on automated market-making and risk-adjusted trading strategies. Valkyrie is recognised for its lean structure and technology-driven execution in both U.S. and European options markets.
27. Kore Trading – United States
Kore Trading is an emerging proprietary firm focused on options and futures markets. The company emphasises innovation through quantitative research and algorithmic design. Kore’s compact team structure allows rapid testing and iteration of new trading models in competitive derivatives markets.
28. Kinetic Trading – United States
Kinetic Trading operates in high-frequency and systematic trading across equities and futures. It prioritises low-latency systems and data-driven execution. The firm’s engineering-first mindset helps it identify short-lived opportunities in fragmented electronic markets.
29. BlackEdge Capital – United States
BlackEdge Capital focuses on options and volatility trading, with a strong quantitative foundation. Based in Chicago, it blends statistical arbitrage, delta hedging, and market microstructure research to optimise execution. Its team combines academic rigour with applied market experience.
30. Mako – United Kingdom
Mako is a London-based derivatives market maker specialising in options and volatility products. The firm provides liquidity in both listed and OTC derivatives across multiple asset classes. Mako’s focus on technology-driven pricing and hedging has made it a trusted participant in European derivatives markets.
31. Edgehog Trading – United States
Edgehog Trading is a high-frequency proprietary firm with a strong emphasis on cross-asset arbitrage and execution algorithms. It employs data scientists and engineers to refine microstructure models that identify latency-sensitive opportunities across exchanges.
32. Boerboel Trading – United States
Boerboel Trading is one of the rising proprietary firms in the HFT space. It trades equities and derivatives using a combination of statistical learning and machine-driven execution. The firm’s success highlights how small, agile prop firms can compete through innovation rather than scale.
33. Vector Trading – United States
Vector Trading represents a new generation of HFT firms built on lightweight, flexible infrastructure. It targets micro-inefficiencies across futures and equities using AI-based prediction and event-driven trading models. Its adaptive framework helps maintain profitability in fast-changing markets.
34. Eschaton Trading – United States
Eschaton Trading operates as a derivatives-focused proprietary firm, active in volatility arbitrage and market-making. The firm leverages data modelling and real-time analytics to navigate complex derivative pricing. Eschaton’s methods balance automation with human supervision for enhanced control.
35. Emergent Trading – United States
Emergent Trading is a Chicago-based prop firm combining quantitative research and discretionary execution. It trades futures and options across major U.S. exchanges. Known for its lean structure, the firm focuses on strategy innovation and capital efficiency.
36. Radix Trading – United States
Radix Trading is a multi-asset proprietary firm with exposure to traditional and crypto markets. It emphasises data analysis, high-speed execution, and cross-venue arbitrage. Radix represents a bridge between conventional quantitative trading and digital asset liquidity.
37. The Voleon Group – United States
Based in Berkeley, California, The Voleon Group applies machine learning techniques to systematic trading. The firm focuses on developing predictive models for the stock market, using large datasets to improve the performance of its strategies over time. While Voleon does not publicly position itself with an explicit “AI-first” mindset, its research emphasis on machine learning is a notable aspect of its approach.
The proprietary and market-making segment represents one of the fastest and most technologically driven areas of global finance. Firms in this space combine quantitative methods, advanced programming, and disciplined capital management to capture small market inefficiencies that occur in very short time frames.
In addition to pursuing returns, these firms also contribute to market structure by providing liquidity, narrowing bid-ask spreads, and supporting more efficient price discovery across asset classes.
4.2. Systematic & Multi-Manager Hedge Funds
Systematic and multi-manager hedge funds are focused on using data-driven models to invest intelligently across the globe. They operate with strict risk controls and are constantly working to build the best possible portfolios for their clients.
Their whole game is about using deep research and powerful technology to find a real, lasting edge in the market, what the pros call alpha. Many of these firms are set up like a collection of small, independent trading teams, or pods, each with its own unique strategy.
38. Two Sigma – United States
Two Sigma integrates data science, AI, and engineering through a global team of quantitative researchers who transform massive datasets into actionable trading insights. Its models analyse equities, futures, and macro markets through predictive algorithms. The firm’s focus on research scalability and disciplined model validation has made it one of the most advanced systematic platforms in the world.
39. Renaissance Technologies – United States
Renaissance Technologies pioneered statistical arbitrage and quantitative modelling, setting the standard for the industry. Known for its top-secret strategies and record-breaking performance, the firm thrives on data precision, automation, and continuous optimisation. Its Medallion Fund remains the benchmark for risk-adjusted returns in quantitative finance.
40. D.E. Shaw & Co. – United States
D.E. Shaw combines scientific research, software engineering, and capital discipline to manage diversified systematic portfolios. The firm’s teams apply risk parity and optimisation models across multiple asset classes. Its long-standing reputation comes from a collaborative culture and deeply integrated technology stack.
41. AQR Capital Management – United States
AQR brings academic finance to large-scale investment management, focusing on factor-based and risk-premia strategies. It emphasises value, momentum, and quality factors while maintaining transparency and cost-efficient execution. AQR’s model stability and disciplined risk controls allow it to manage billions across institutional mandates.
42. Squarepoint Capital – United States
Squarepoint Capital operates multi-asset systematic programs combining medium-frequency statistical models and futures arbitrage. The firm’s strength lies in its signal diversification, capacity discipline, and precise execution. Its data-driven research process is supported by cross-team infrastructure built for consistency and scalability.
43. PDT Partners – United States
Emerging from Morgan Stanley’s quant division, PDT Partners is now an independent firm known for rigorous experimentation and strong model governance. Its culture rewards collaboration and scientific integrity, emphasising robust code, backtesting quality, and production reliability. PDT’s long-term consistency stems from continuous iteration rather than rapid expansion.
44. TGS Management – United States
TGS Management remains one of the most discreet yet enduring quantitative investment firms. It focuses on statistical rigour and long-term alpha persistence, preferring small research teams and measured scalability. Its process-driven approach emphasises robust validation, stable Sharpe ratios, and minimal operational noise.
45. G-Research – United Kingdom
London-based G-Research specialises in predictive modelling for equity markets, using machine learning, NLP, and high-performance computing. Its research culture is built on collaboration between data scientists and quants. The firm’s academic rigour and cutting-edge technology make it one of Europe’s leading quantitative research houses.
46. Man Numeric – United States
Man Numeric, part of the Man Group, focuses on quantitative equity investing that integrates ESG and factor-based approaches. Its process blends short-term alpha signals with long-term portfolio optimisation. The firm’s edge comes from precise risk decomposition and continual enhancement of its model architecture.
47. Man AHL – United Kingdom
Man AHL pioneered managed futures and trend-following before expanding into broader systematic investing. It runs models across macro, commodities, and alternative risk premia, adapting to shifting volatility regimes. With deep research depth and real-time risk systems, AHL remains a cornerstone of global quant macro trading.
48. Winton Group – United Kingdom
Founded by David Harding, Winton evolved from a pure trend follower into a multi-strategy scientific investment firm. It applies Bayesian inference and data-driven analysis to find persistent relationships in markets. Winton’s disciplined focus on evidence-based research defines its enduring credibility among institutional allocators.
49. Aspect Capital – United Kingdom
Aspect Capital manages systematic macro and managed-futures portfolios, designed to perform across market cycles. Its process emphasises transparency, diversification, and volatility targeting. Aspect’s disciplined drawdown management and adaptive signal calibration make it a reliable diversifier in institutional portfolios.
50. Arrowstreet Capital – United States
Arrowstreet Capital runs quantitative global equity portfolios based on multifactor stock-selection models. Its focus is on capacity management and alpha durability through disciplined rebalancing. The firm’s reputation rests on long-term stability and rigorous execution analytics.
51. PanAgora Asset Management – United States
PanAgora blends quantitative methods with behavioural insights, developing multi-factor equity and multi-asset strategies. Its approach integrates risk-based modelling and client customisation to meet institutional goals. PanAgora stands out for its emphasis on innovative factor combinations and robust validation frameworks.
52. Qube Research & Technologies – United Kingdom
Qube operates a global multi-asset platform focusing on adaptive modelling and data integrity. Its research teams deploy independent systematic strategies under a shared infrastructure. With expertise in futures, equities, and cross-asset alpha, Qube is known for balancing innovation with careful risk budgeting.
53. Quantitative Investment Management – United States
This Charlottesville-based firm specialises in systematic macro and futures-driven strategies. It applies probabilistic forecasting and scenario testing to adapt to shifting market conditions. Quantitative Investment Management’s consistent results come from a disciplined emphasis on capital allocation and volatility normalisation.
54. Quantlab Financial – United States
Quantlab is a technology-first trading firm bridging low-latency execution and medium-frequency modelling. Its research integrates real-time feedback loops that refine model performance intraday. Quantlab’s ability to merge engineering precision and quantitative insight keeps it competitive among elite systematic players.
55. Quantbot Technologies – United States
Quantbot builds machine-learning-driven strategies across global equity and futures markets. Its modular research environment supports rapid testing, feature discovery, and cross-asset model validation. The firm’s collaborative structure allows quants and engineers to iterate quickly and scale successful signals efficiently.
56. Quantbox Research – United States
Quantbox Research represents the new generation of agile systematic firms. It emphasises signal discovery, statistical arbitrage, and adaptive modelling with tight feedback cycles. Its focus on interpretability and clean infrastructure enables scalable execution across multiple venues.
57. Millennium Management – United States
Millennium operates one of the world’s largest multi-manager hedge fund platforms, hosting both systematic and discretionary pods. Each team manages independent portfolios under strict risk limits and capital allocation rules. The firm’s consistency stems from process discipline and centralised oversight.
58. Point72 (Cubist Systematic Strategies) – United States
Cubist, the systematic arm of Point72, develops data-driven equity and futures models under the same pod-based structure. It invests heavily in quant research, data engineering, and infrastructure. The team’s strength lies in scientific rigour and an adaptive research culture.
59. Balyasny Asset Management (BAM) – United States
BAM integrates quantitative and discretionary strategies across multiple pods. Its systematic teams focus on signal diversification and execution quality. The firm’s centralised risk management ensures controlled exposure and resilience during market shocks.
60. Schonfeld Strategic Advisors – United States
Schonfeld has expanded its systematic and quantitative divisions while maintaining diversified multi-manager operations. It prioritises cross-pod collaboration and model transparency. Schonfeld’s disciplined hiring and infrastructure investment underpin its steady growth in the quant sector.
61. ExodusPoint Capital – United States
ExodusPoint runs systematic macro, equity, and multi-strategy portfolios within a risk-controlled framework. The firm emphasises governance, liquidity awareness, and cross-team integration. Its balance between discretion and quantitative precision defines its appeal among institutional investors.
62. WorldQuant – United States
WorldQuant operates a global network of distributed researchers building and testing alpha signals. It aggregates thousands of predictive models into diversified portfolios. The firm’s focus on data quality, orthogonality, and process automation allows it to scale globally without losing efficiency.
63. Verition Fund Management – United States
Verition combines systematic and discretionary strategies under a unified capital management structure. Its growing quant division specialises in macro, relative-value, and statistical arbitrage. A conservative approach to drawdowns and risk exposure ensures steady performance across cycles.
64. Laurion Capital Management – United States
Laurion Capital employs volatility-aware and event-driven quantitative models. Its trading framework blends correlation analysis, hedging, and risk targeting. The firm’s disciplined capital allocation supports strong resilience in turbulent market phases.
65. Capstone Investment Advisors – United States
Capstone focuses on systematic derivatives and volatility strategies across global markets. It combines quantitative research with macro risk overlays to manage portfolio variance. The firm’s expertise in options and volatility modelling reinforces its leadership in alternative risk premia.
66. Brevan Howard (Systematic Division) – United Kingdom
Brevan Howard’s systematic team complements its traditional macro operations. It uses data-driven models in rates, FX, and futures to enhance diversification. The division integrates machine learning and automation into a historically discretionary framework, reflecting the evolution of macro trading.
67. Quadrature Capital – United Kingdom
Quadrature applies machine-learning techniques and multi-horizon models to global equity trading. Its process prioritises stability, validation, and drawdown control over short-term gain. The firm’s focus on scalable infrastructure and research repeatability ensures steady returns.
68. Vatic Investments – United States
Vatic Investments combines ML research, microstructure analytics, and low-latency execution in a unified system. It develops proprietary data pipelines that support real-time model calibration. Vatic’s focus on innovation and research velocity makes it one of the most technically advanced new-generation quant funds.
69. Dark Forest Technologies – United States
Dark Forest uses AI-driven ensemble modelling and feature engineering to uncover predictive relationships in financial data. It enforces strict overfitting controls and stability checks across all models. The firm’s commitment to research transparency and rigorous validation defines its modern quant identity.
70. Aquatic Capital Management – United States
Aquatic Capital applies systematic multi-asset strategies emphasising signal orthogonality and balanced exposure. Its teams focus on clean data processing, execution precision, and post-trade analytics. The firm’s research-driven culture encourages steady improvement and controlled scaling.
71. Capula Investment Management – United Kingdom
Capula’s systematic group functions in support of the firm’s principal macro discretionary and rates-driven strategies, rather than as a standalone quantitative fund. The group develops models for interest rates, volatility, and term-structure dynamics that augment the firm’s macro research and inform institutional portfolio management.
Through the integration of discretionary macro expertise with quantitative methodologies, and with a sustained focus on tail-risk mitigation and liquidity discipline, Capula upholds its reputation as a highly reliable and defensive allocator.
72. Paloma Partners – United States
Paloma Partners manages diversified quantitative and discretionary strategies under unified risk governance. It emphasises capital efficiency, resilience, and drawdown control. Paloma’s focus on balanced exposure and structured oversight supports stable long-term performance.
73. Rokos Capital Management – United Kingdom
Rokos employs selective systematic tools to support its macro investment process, using them primarily to enhance decision quality and risk awareness. These models play a complementary role, while discretionary judgment remains central to portfolio construction.
The firm’s focus on capital preservation and disciplined volatility management continues to underpin its consistent performance.
74. RSJ – Czech Republic
RSJ operates as a European quantitative derivatives fund, active in futures and options arbitrage. It uses volatility modelling and hedging techniques to exploit market inefficiencies. The firm’s disciplined capital allocation and liquidity management underpin its reliability in derivatives trading.
75. Freestone Grove Partners – United States
Freestone Grove Partners is an emerging multi-strategy quant firm developing equity and futures programs. Its researchers focus on machine learning, rigorous backtesting, and alpha scalability. The firm’s lean, research-focused setup supports fast iteration while maintaining strict risk governance.
76. Summerside Capital – United States
Summerside Capital specialises in quantitative equity strategies that balance alpha diversification and cost control. Its models emphasise factor exposure, low turnover, and execution efficiency. Summerside’s methodical process enables stable results across both calm and volatile markets.
This group of systematic and multi-manager hedge funds defines the modern landscape of quantitative investing. Each firm transforms massive datasets into structured, risk-adjusted performance through rigorous research, portfolio discipline, and scalable technology.
4.3. Asset Managers & Institutional Quant Divisions
Asset managers and institutional investment firms represent the long-term, capital-intensive side of quantitative finance. Unlike hedge funds that pursue short-term inefficiencies, these institutions use systematic, factor-based models to build scalable, risk-controlled portfolios.
Their focus is on stability, governance, and consistency, using quantitative research to enhance active management, asset allocation, and risk-adjusted returns for pension funds, endowments, and sovereign clients.
77. BlackRock (Systematic Equities & Fixed Income) – United States
BlackRock’s systematic division manages one of the world’s largest pools of quantitative equity and fixed-income strategies. It combines factor investing, AI-based optimisation, and macro modelling within its Aladdin platform. The team’s strength lies in data integration and ESG analytics, delivering precision portfolio management at a global scale.
78. PGIM Quant Solutions – United States
Formerly known as QMA, PGIM Quant Solutions applies multi-factor models and behavioural finance frameworks to global equities and multi-asset portfolios. Its strategies emphasise long-horizon alpha and downside risk control. PGIM’s blend of academic research and institutional governance ensures performance consistency for large asset owners.
79. AllianceBernstein (AB Quant) – United States
AB Quant integrates quantitative research and machine learning into its equity, credit, and multi-asset platforms. Its approach prioritises data transparency, liquidity modelling, and predictive analytics. AB’s investment philosophy merges fundamental insight with systematic execution, producing risk-aware strategies for institutional clients.
80. Man Group – United Kingdom
Man Group operates as a parent organisation for AHL and Numeric, combining both systematic and discretionary divisions. It runs quantitative equity, macro, and multi-asset strategies through integrated risk and research systems. The firm’s technology-driven culture and long history in systematic investing make it a global benchmark for quant asset management.
81. Wellington Management (Quant Division) – United States
Wellington’s quantitative division leverages factor research and predictive analytics to enhance active strategies. Its models assess valuation, momentum, and risk premia across global equity and fixed-income markets. Wellington’s collaborative structure enables quant teams to support fundamental managers, bridging analytics with human judgment.
82. HSBC Quant Investment Solutions – United Kingdom
HSBC’s Quant Investment Solutions team designs systematic equity and fixed-income portfolios tailored to institutional mandates. It applies rule-based strategies, volatility targeting, and macro factor modelling. HSBC’s advantage lies in its global data access and multi-asset infrastructure, serving both corporate and institutional investors.
83. AlphaSimplex (Virtus Investment Partners) – United States
Now part of Virtus Investment Partners, AlphaSimplex specialises in systematic trend-following and managed-futures strategies. Its research blends market volatility dynamics with risk parity concepts. The firm’s disciplined risk management and adaptive models make it a trusted solution for volatility-hedging mandates.
84. GAM Systematic – Switzerland
GAM Systematic runs a diverse range of quantitative macro and multi-asset programs. Its philosophy revolves around pattern recognition, portfolio diversification, and scenario analysis. By combining data science and risk control, GAM’s team maintains a steady performance profile suitable for institutional allocators.
85. CQS – United Kingdom
CQS operates quantitative and hybrid credit strategies, supported by advanced analytics and macro factor modelling. It uses systematic portfolio construction and credit risk scoring to manage exposure across structured products and fixed income. The firm’s strong governance ensures a consistent risk-return balance within complex credit markets.
86. Graham Capital Management (Systematic Macro) – United States
Graham Capital integrates systematic macro models alongside its discretionary macro portfolio. Its strategies cover rates, FX, and commodities, emphasising diversification and volatility targeting. The firm’s infrastructure supports model blending and dynamic risk allocation, ensuring robustness through different market regimes.
87. Bridgewater Associates (Systematic Components) – United States
Bridgewater, the world’s largest hedge fund, incorporates systematic components into its macro framework. It leverages data analytics and factor-based modelling to complement its discretionary insights. The firm’s culture of process transparency and stress-testing reflects the rigour behind its systematic risk analysis.
88. Ares Management (Quant Fixed Income Team) – United States
Ares Management’s quant fixed-income team employs statistical modelling, duration analysis, and factor attribution to manage large credit portfolios. Its goal is to optimise yield, liquidity, and risk-adjusted spread performance. Ares combines quantitative precision with deep market knowledge of structured credit and corporate bonds.
89. QVR Advisors – United States
QVR Advisors has carved out a niche in the complex world of volatility trading. Instead of just betting on market direction, their models are built to profit from market swings and protect portfolios from unexpected crashes.
They specialise in sophisticated options strategies, essentially acting as the insurance policy for their institutional clients against extreme market events.
90. Sensato Investors – United States
Sensato Investors specialises in quantitative equity strategies in Asian markets, integrating fundamental overlays with quantitative stock selection. Its models capture regional inefficiencies using factor momentum and liquidity analytics. Sensato’s niche expertise provides localised exposure within a global quant framework.
The quantitative divisions within major asset managers bring scientific discipline to long-term investing. Their goal is not to outpace markets overnight but to enhance consistency, transparency, and scalability through models that adapt over years, not seconds.
4.4. Crypto & Digital Asset Trading Firms
Crypto-native firms bring the discipline of quantitative analysis to the chaotic, 24/7 world of blockchain. They take proven strategies like market-making and arbitrage and adapt them for a decentralised landscape where speed and security are everything. These are the firms applying data science and high-speed tech to reshape the future of finance.
91. Wintermute – United Kingdom
Wintermute is one of the largest digital asset market makers globally, providing liquidity across centralised exchanges and DeFi protocols. The firm’s infrastructure combines ultra-low-latency systems and adaptive algorithms, enabling efficient pricing for thousands of trading pairs.
Wintermute’s technology-driven execution and deep capital reserves make it a cornerstone of the crypto market structure worldwide.
92. Wincent Trading – Europe
Wincent Trading operates as a quantitative crypto trading desk, applying systematic strategies to both spot and derivatives markets. It focuses on cross-venue arbitrage, basis trading, and high-frequency market making, supported by advanced data analytics.
The firm’s modular infrastructure allows rapid deployment of models across volatile digital markets while maintaining strict risk discipline.
93. GSR Markets – Hong Kong
GSR is a pioneering crypto-native trading firm and market maker founded in 2013. Operating globally, it provides deep liquidity for thousands of digital assets across centralised and decentralised exchanges.
The firm combines sophisticated quantitative models, low-latency execution, and a large balance sheet to support institutional clients and token projects. GSR’s activities also extend to venture capital, investing in promising early-stage blockchain technologies.
94. Galaxy Trading – United States
Galaxy Trading, the team that handles trading for Galaxy Digital, operates across the full spectrum of crypto, from spot to futures and options. Their edge comes from using sophisticated models to execute trades cleanly, anticipate volatility, and get a deeper read on the market’s structure.
With strong institutional backing, Galaxy has carved out a niche as a key link between the old world of finance and the new world of digital assets.
Firms are pioneering what it means to be a quant in the crypto space. They’re combining the speed of high-frequency trading with blockchain’s unique infrastructure, where success often hinges on smart liquidity solutions and a rock-solid risk plan.
4.5. Rising Quant & AI-Driven Firms
Rising quant and AI-driven firms are reshaping finance by prioritising machine learning, automation, and experimental data science. Unlike legacy quants, these firms evolve rapidly, testing new architectures like deep reinforcement learning, ensemble modelling, and neural optimisation. Their agility and innovation culture position them as the research frontier of next-generation systematic trading.
95. Numerai – United States
Numerai is a San Francisco-based AI-run hedge fund that pioneers a crowdsourced approach to quantitative trading. Instead of internal secrecy, it provides encrypted financial data to a global network of data scientists who compete to build the best predictive models.
Numerai aggregates these contributions into a meta-model to trade global equities, bridging the gap between decentralised data science and institutional capital.
96. Headlands Technologies – United States
Headlands Technologies is a global quantitative trading firm headquartered in Chicago and San Francisco. The firm is known for its disciplined scientific approach and high-performance infrastructure.
Headlands focuses on developing automated trading strategies across multiple asset classes. It emphasises rigorous code quality and low-latency execution to capture market inefficiencies.
97. Rosetta Analytics – United States
Rosetta Analytics applies deep learning and behavioural modelling to predict cross-asset performance. It leverages AI interpretable frameworks to enhance transparency in institutional investing, translating complex neural outputs into actionable insights.
Rosetta’s hybrid approach, combining quantitative rigour with explainable AI, bridges the gap between machine prediction and portfolio accountability.
98. Trexquant – United States
Trexquant is a systematic hedge fund that leverages a global research network to generate trading signals. Through its unique Trexquant Accelerator program, the firm sources thousands of alpha signals from data scientists worldwide.
It uses advanced machine learning techniques to combine these signals into diversified equity portfolios, allowing for rapid adaptation to changing market regimes.
99. Blueshift Asset Management – United States
Blueshift is a systematic investment firm that applies advanced machine learning and statistical modelling techniques to trade global financial markets. Headquartered in New Jersey, the firm’s research-driven culture focuses on discovering persistent alpha signals from vast and complex datasets.
Blueshift’s strategies are designed to be market-neutral and decorrelated from traditional asset classes, emphasising rigorous scientific validation and risk management in its automated portfolio construction.
100. Crabel Capital Management – United States
Crabel Capital Management bridges systematic trading and behavioural finance, managing global futures and FX strategies. Its models rely on statistical learning, volatility clustering, and trend persistence, refined through decades of research.
Crabel’s disciplined process of model validation and risk-adjusted optimisation makes it a leader in short-term, adaptive quant investing.
The rise of AI-native quant firms marks a shift from traditional statistical modelling to autonomous, adaptive intelligence. These organisations merge deep learning and real-time optimisation to create faster, smarter trading systems. In 2026, they embody the next phase of quantitative evolution, where finance meets artificial cognition.
5. How quantitative trading firms evaluate traders
In a top quant firm, judging a trader’s performance is about way more than just looking at their profit and loss. It’s a deep dive into their process, risk discipline, and ability to innovate. They use a structured approach to see if a trader is just lucky, or if they have a real, repeatable edge.
5.1. Key evaluation criteria
Before diving into the process, firms define the main areas to measure a trader’s performance:
- Are you making money consistently? Profitability is the starting point, but they look for a steady track record, not just one big win.
- Do you follow the rules? This is huge. They track how well a trader respects risk limits, drawdowns, and stop-losses. A profitable but reckless trader won’t last long.
- Are your returns worth the risk? Using metrics like the Sharpe ratio, they figure out if the profit generated was worth the rollercoaster ride to get it.
- Are you actually skilled? They measure a trader’s “alpha” to see if their performance is beating the market benchmarks, or just moving with the tide.
- Can you find new ideas? The best quants are always improving. The firm wants to see that a trader can create new strategies, test them, and make existing ones better.
- How clean are your trades? They monitor things like slippage to see how efficiently a trader’s orders are being executed in the live market.
5.2. Evaluation process
Once those criteria are clear, the process for vetting a new trading idea is intense:
- Idea generation: Traders propose new strategies or improvements.
- Research & backtesting: Quants test these strategies against historical data to verify potential.
- Modelling & risk assessment: Strategies are modelled for risk alignment and stress-tested under various conditions.
- Live trading & monitoring: Backtested strategies are deployed with real capital while performance is tracked in real time.
- Performance analysis: Results are analysed using metrics such as PnL, Sharpe Ratio, and execution efficiency. Feedback is applied to optimise both the trader’s approach and algorithmic models.
This whole system is designed to build discipline. It creates an environment where traders are rewarded for a solid process and constant improvement, not just for getting lucky. That’s the only way to survive long-term in these markets.
6. What are the challenges & risks for quantitative trading firms in 2026?
The very things that make quant firms so powerful are also their biggest vulnerabilities. In today’s market, the same technology that can generate enormous profits can also amplify a small mistake into a catastrophic failure. Staying competitive is no longer just about being the smartest; it’s about being the most resilient.

- Model overfitting and bias: A huge danger is overfitting, creating a model that’s brilliant at explaining yesterday’s market but completely useless for predicting tomorrow’s. To fight this, firms have to constantly test their ideas on data they’ve never seen before to make sure they haven’t just memorised the past.
- Market volatility and liquidity risk: During periods of high volatility, algorithms can respond too quickly, leading to self-reinforcing losses or flash events. Robust liquidity modelling coupled with circuit breakers should help prevent systems from compounding short-term disruptions.
- Technology and infrastructure failures: Heavy dependence on low-latency systems and co-located servers makes firms vulnerable to outages or cyber threats. Leading players deploy redundant networks, backup systems, and AI-based monitoring to minimise downtime.
- Regulatory and compliance pressure: Regulators around the world now demand to know how these complex algorithms work. This adds a huge layer of compliance work and legal risk to every strategy.
- Talent and competition: The demand for quant researchers and AI engineers far exceeds supply, driving up costs and turnover. Many firms now invest in internal training and academic collaboration to sustain research capacity.
- Model drift and adaptation: Markets change more quickly than fixed models can adapt to. Constant retraining, recalibration, and ensemble learning help maintain performance as correlations and volatility shift.
The biggest risks now come from this crushing complexity of speed, data, and technology. The firms that will survive and thrive are those that can see trouble coming, adapt on the fly, and manage their systems with extreme discipline. The new edge is about being smarter and more resilient than everyone else.
Traders can also improve their edge by learning how to trade using indicators effectively, helping them avoid common mistakes.
7. Why quantitative trading firms matter in today’s markets
It’s easy to overlook quant firms, but they’ve become the essential plumbing of modern finance. They use a mix of math and technology to change how money and risk move through the markets. The result is a system that reacts faster, manages risk more logically, and runs smoothly even when things get chaotic.
- Liquidity and market efficiency: Quant firms make sure there’s almost always someone on the other side of your trade. By always being ready to buy and sell, they shrink the gap between prices, which means everyone gets a fairer, more efficient deal.
- Innovation and technology advancement: The constant need for a tiny advantage means these firms are always pushing the limits of technology. Their work has led to new ideas in AI, data analysis, and high-speed computing that are now used in many other fields.
- Risk management and stability: When markets get chaotic, human emotion often takes over. Quant firms are different. Because their strategies are built on data and rules, they can help absorb panic instead of adding to it, bringing a measure of stability when it’s needed most.
- Diversification and market depth: These firms don’t just stick to one market. They trade everything from stocks to crypto all over the world. This helps balance out the entire system, making sure that money can flow to where it’s needed.
- Talent and research ecosystem: These firms have become a gathering place for some of the sharpest minds from science and tech. They bring together people from different fields to solve complex problems, which helps push the entire financial industry forward.
You might not always see them, but quant firms are the invisible infrastructure of modern finance. By providing liquidity, advancing technology, and bringing a data-first mindset to trading, they make the markets more open and reliable for all of us.
For traders who want a broader view of the ecosystem, it helps to explore how prop firms make money. Learning how to set up a prop trading firm also provides useful insight into how these models shape today’s market structure.
8. Tips to stay consistent in Quantitative Trading
The funny thing about quant trading is that even with all the automation, your success still comes down to discipline and a good routine. That’s honestly the hardest part, and it’s where most people trip up. Here’s how the pros stay on track.
- Create your playbook, and stick to it: Every solid strategy needs a rulebook. Write down everything: when you get in, when you get out, how much you risk. This playbook becomes your anchor when the market gets chaotic and stops you from making decisions based on fear.
- Let the machines do the work: Automate as much as you can. Doing this takes your own biases and bad habits out of the picture. It makes sure your plan is followed exactly as you designed it, which is a lifesaver when things get hectic.
- Schedule your check-ups: You have to set a fixed time to review your performance, maybe every week or month. This is when you check your stats, win rate, drawdowns, and slippage. This simple routine is how you spot a good strategy that’s starting to go stale.
- Have an undo button: Always use version control for your code and models. It’s a simple way to track changes. If a new tweak doesn’t work out, you can easily go back to the last version that did.
- Don’t trade yesterday’s market: Markets are always changing. What worked last month might not work today. Staying on top of things isn’t just about headlines; it’s about making sure your strategy is still a good fit for the current market.
- Watch the small stuff: Tiny issues like trade delays or slippage might not seem like a big deal, but they can slowly eat away at your profits. Keep an eye on them.
- Keep it simple: It’s easy to fall into the trap of making your strategy overly complex to chase a perfect backtest. Often, the toughest strategies are the simplest ones that work well, no matter what the market is doing.
- Follow the data, not your gut: Before you change a strategy that’s already working, ask yourself one question: Is this change based on real data, or is it just a hunch? Let the numbers guide you.
It all comes down to building a solid system around your trading. When your rules are clear, your trades are automated, and you review everything regularly, you create a space where your models, not your gut feelings, are in charge. That’s the secret to lasting in this game.
9. FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions
A quantitative trading firm uses data, algorithms, and automation to make trades, while hedge funds often rely on human judgment and discretionary analysis. Quant firms make decisions based on code and models rather than emotions or market opinions.
They profit by identifying small, repeatable price inefficiencies across markets. Using algorithms, they trade large volumes at high speed, earning from arbitrage, market-making, and trend-based strategies.
Common strategies include high-frequency trading (HFT) for micro-price movements, statistical arbitrage for pricing gaps, and market-making for liquidity. Others apply trend-following, mean reversion, or AI-driven prediction models.
No. A PhD helps in research-heavy roles, but firms also hire candidates with strong math, coding, and problem-solving skills from bachelor’s or master’s programs.
Firms like Jane Street, Optiver, HRT, IMC, and Akuna Capital offer graduate and internship programs with hands-on training in trading, modelling, and risk management.
Most start as analysts or developers, then move to trader or portfolio manager roles. Entry pay averages $150K–$200K, with bonuses often doubling that for top performers.
They use low-latency systems, cloud computing, machine learning, and alternative data such as sentiment or transaction data to find trade signals and execute orders in milliseconds.
Key risks include model overfitting, data errors, regulatory pressure, and rising tech costs. Firms also face intense competition for skilled data scientists and quant researchers.
Strong knowledge of math, statistics, and programming (Python, C++, SQL) is crucial. Understanding financial markets and risk management helps turn theory into practical trading models.
Machine learning enables models to adapt faster and find complex patterns unseen by traditional analysis. It drives the shift toward self-learning, AI-driven trading systems across major quant firms.
There isn’t a single biggest quant trader, as many top professionals work within firms rather than publicly. Some well-known figures include Jim Simons of Renaissance Technologies, who built the Medallion Fund, famous for consistently high returns using quantitative strategies.
No, it’s not too late. While many start earlier, strong skills in math, programming, and financial modelling can allow someone to enter the field later. Continuous learning and real-world project experience are key to breaking in.
Prop firms assess traders based on profitability, risk management, consistency, and adherence to firm rules. Performance metrics like PnL, drawdown, Sharpe ratio, and execution efficiency are monitored, and traders may undergo backtesting or live performance evaluation.
Yes. Many prop firms encourage or even require algorithmic trading, especially in quantitative or high-frequency strategies. Traders must ensure algorithms comply with the firm’s risk limits and trading rules.
No. Rules differ by firm and by account type. Each prop firm sets its own risk limits, leverage rules, profit targets, and consistency requirements. Understanding these rules is essential before joining or funding an account.
Track key metrics like weekly PnL, drawdown, Sharpe ratio, and win/loss ratios. Many firms provide dashboards or reporting tools to review execution quality, adherence to risk limits, and overall stability over time.
10. Conclusion
By 2026, Quantitative Trading Firms will no longer just influence the market; they will actively define it. By turning data and automation into a core strategic advantage, they have introduced a new era of speed and intelligence to trading. This has firmly established them as the new leaders in finance, setting a higher bar for performance and efficiency across the entire industry.
For anyone involved in the markets, the success of the top quantitative trading firms in 2026 highlights a crucial truth: a deep understanding of technology is now essential. The new benchmark for success is set by those who can master speed, demand accuracy, and maintain unwavering control over risk.
To explore more about prop trading and algorithmic strategies, visit the Prop Firm & Trading Strategies section at H2T Funding. You’ll find clear, practical guides to help you understand the world of professional trading and build your own path in quantitative finance.